🔗Asymptote Gallery Tagged by “Graph (3D)” #151
🔗animations-fig007
Show animations/fig0080.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Animation
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Function (graphing) | #Animation | #Sphere | #Surface | #Path3 | #Segment
size(16cm); import graph3; import animation; import solids; settings.render=0; animation A; int nbpts=500; real q=2/5; real pas=5*2*pi/nbpts; int angle=3; real R=3; real x(real t){return R*cos(q*t)*cos(t);} real y(real t){return R*cos(q*t)*sin(t);} real z(real t){return R*sin(q*t);} triple[] P; real t=-pi; for (int i=0; i<nbpts; ++i) { t+=pas; P.push((x(t),y(t),z(t))); } currentprojection=orthographic((0,5,2)); currentlight=(3,3,5); pen p=rgb(0.1,0.1,0.58); transform3 t=rotate(angle,(0,0,0),(1,0.25,0.25)); filldraw(box((-R-0.5,-R-0.5),(R+0.5,R+0.5)), p, 3mm+black+miterjoin); revolution r=sphere(O,R); draw(surface(r),p); for (int phi=0; phi<360; phi+=angle) { bool[] back,front; save(); for (int i=0; i<nbpts; ++i) { P[i]=t*P[i]; bool test=dot(P[i],currentprojection.camera) > 0; front.push(test); } draw(segment(P,front,operator ..),linewidth(1mm)); draw(segment(P,!front,operator ..),grey); A.add(); restore(); } A.movie();
🔗animations-fig008
Show animations/fig0090.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Animation
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Function (graphing) | #Animation | #Sphere | #Surface | #Path3 | #Segment | #Projection (3D) | #Plane
size(16cm); import graph3; import animation; import solids; currentlight.background=black; settings.render=0; animation A; A.global=false; int nbpts=500; real q=2/5; real pas=5*2*pi/nbpts; int angle=4; real R=0.5; pen p=rgb(0.1,0.1,0.58); triple center=(1,1,1); transform3 T=rotate(angle,center,center+X+0.25*Y+0.3*Z); real x(real t){return center.x+R*cos(q*t)*cos(t);} real y(real t){return center.y+R*cos(q*t)*sin(t);} real z(real t){return center.z+R*sin(q*t);} currentprojection=orthographic(1,1,1); currentlight=(0,center.y-0.5,2*(center.z+R)); triple U=(center.x+1.1*R,0,0), V=(0,center.y+1.1*R,0); path3 xy=plane(U,V,(0,0,0)); path3 xz=rotate(90,X)*xy; path3 yz=rotate(-90,Y)*xy; triple[] P; path3 curve; real t=-pi; for (int i=0; i < nbpts; ++i) { t+=pas; triple M=(x(t),y(t),z(t)); P.push(M); curve = curve..M; } curve=curve..cycle; draw(surface(xy), grey); draw(surface(xz), grey); draw(surface(yz), grey); triple xyc=(center.x,center.y,0); path3 cle=shift(xyc)*scale3(R)*unitcircle3; surface scle=surface(cle); draw(scle, black); draw(rotate(90,X)*scle, black); draw(rotate(-90,Y)*scle, black); draw(surface(sphere(center,R)), p); triple vcam=1e5*currentprojection.camera-center; for (int phi=0; phi<360; phi+=angle) { bool[] back,front; save(); for (int i=0; i<nbpts; ++i) { P[i]=T*P[i]; bool test=dot(P[i]-center,vcam) > 0; front.push(test); } curve=T*curve; draw(segment(P,front,operator ..), paleyellow); draw(segment(P,!front,operator ..),0.5*(paleyellow+p)); draw((planeproject(xy)*curve)^^ (planeproject(xz)*curve)^^ (planeproject(yz)*curve), paleyellow); A.add(); restore(); } A.movie();
🔗graph3-fig001
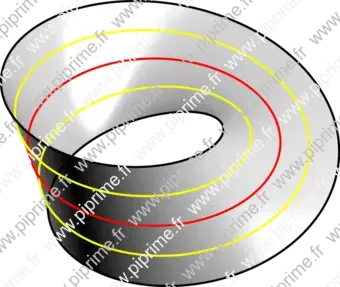
A Möbius strip of half-width with midcircle of radius
and at height can be represented parametrically by :
for in and in . In this parametrization, the Möbius strip is therefore a cubic surface with equation
Source
Show graph3/fig0010.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Surface | #Level set (3D)
import graph3; ngraph=200; size(12cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(-4,-4,5); real x(real t), y(real t), z(real t); real R=2; void xyzset(real s){ x=new real(real t){return (R+s*cos(t/2))*cos(t);}; y=new real(real t){return (R+s*cos(t/2))*sin(t);}; z=new real(real t){return s*sin(t/2);}; } int n=ngraph; real w=1; real s=-w, st=2w/n; path3 p; triple[][] ts; for (int i=0; i <= n; ++i) { xyzset(s); p=graph(x,y,z,0,2pi); ts.push(new triple[] {}); for (int j=0; j <= ngraph; ++j) { ts[i].push(point(p,j)); } s += st; } pen[] pens={black, yellow, red, yellow, black}; draw(surface(ts, new bool[][]{}), lightgrey); for (int i=0; i <= 4; ++i) { xyzset(-w+i*w/2); draw(graph(x,y,z,0,2pi), 2bp+pens[i]); }
🔗graph3-fig002

Show graph3/fig0020.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import graph3; size(8cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(1,1,1); limits((0,-2,0),(2,2,2)); xaxis3("$x$", OutTicks()); yaxis3("$y$", OutTicks()); zaxis3("$z$", OutTicks());
🔗graph3-fig003

Show graph3/fig0030.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import graph3; size(8cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(1,1,1); limits((0,-2,0), (2,2,2)); axes3("$x$","$y$","$z$",Arrow3);
🔗graph3-fig004

Show graph3/fig0040.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import graph3; size(8cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(1,1,1); defaultpen(overwrite(SuppressQuiet)); limits((0,-2,0),(2,2,2)); xaxis3("$x$", InTicks(XY()*Label)); yaxis3("$y$", InTicks(XY()*Label)); zaxis3("$z$", OutTicks, p=red, arrow=Arrow3);
🔗graph3-fig005

Show graph3/fig0050.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import graph3; size(6cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(1,1,1); limits((-2,-2,0),(0,2,2)); xaxis3(Label("$x$",MidPoint), OutTicks()); yaxis3("$y$", InTicks()); zaxis3("$z$",XYEquals(-2,0), OutTicks());
🔗graph3-fig006

Show graph3/fig0060.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import graph3; usepackage("icomma"); size(8cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(1.5,1,1); limits((-2,-1,-.5), (0,1,1.5)); xaxis3("$x$", Bounds(Both,Value), OutTicks(endlabel=false)); yaxis3("$y$", Bounds(Both,Value), OutTicks(Step=.5,step=.25)); zaxis3("$z$", XYEquals(-2,0), InOutTicks(Label(align=Y-X))); dot(Label("",align=Z), (-1,0,0), red);
🔗graph3-fig007

Show graph3/fig0070.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Axis (3D) | #Triple
import graph3; size(8cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(1,1,0.5); limits((-2,-2,0),(0,2,2)); xaxis3(Label("$x$",align=Z), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks(endlabel=false,Step=1,step=0.5)); yaxis3("$y$", Bounds(), OutTicks(pTick=0.8*red, ptick=lightgrey)); zaxis3("$z$", Bounds(), OutTicks, p=red, arrow=Arrow3); dot(Label("",align=Z), (-1,0,0), red);
🔗graph3-fig008

Show graph3/fig0080.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Surface | #Level set (3D) | #Contour | #Function (implicit)
// Adapted from the documentation of Asymptote. import graph3; import contour; texpreamble("\usepackage{icomma}"); size3(12cm, 12cm, 8cm, IgnoreAspect); real sinc(pair z) { real r=2pi*abs(z); return r != 0 ? sin(r)/r : 1; } limits((-2, -2, -0.2), (2, 2, 1.2)); currentprojection=orthographic(1, -2, 0.5); xaxis3(rotate(90, X)*"$x$", Bounds(Min, Min), OutTicks(rotate(90, X)*Label, endlabel=false)); yaxis3("$y$", Bounds(Max, Min), InTicks(Label)); zaxis3("$z$", Bounds(Min, Min), OutTicks()); draw(lift(sinc, contour(sinc, (-2, -2), (2, 2), new real[] {0})), bp+0.8*red); draw(surface(sinc, (-2, -2), (2, 2), nx=100, Spline), lightgray); draw(scale3(2*sqrt(2))*unitdisk, paleyellow+opacity(0.25), nolight); draw(scale3(2*sqrt(2))*unitcircle3, 0.8*red);
🔗graph3-fig009
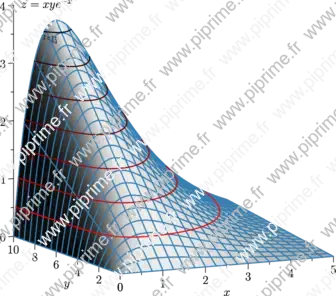
Show graph3/fig0090.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Surface | #Level set (3D) | #Contour | #Function (implicit) | #Palette
size(12cm,0,false); import graph3; import contour; import palette; texpreamble("\usepackage{icomma}"); real f(pair z) {return z.x*z.y*exp(-z.x);} currentprojection=orthographic(-2.5,-5,1); draw(surface(f,(0,0),(5,10),20,Spline),palegray,bp+rgb(0.2,0.5,0.7)); scale(true); xaxis3(Label("$x$",MidPoint),OutTicks()); yaxis3(Label("$y$",MidPoint),OutTicks(Step=2)); zaxis3(Label("$z=xye^{-x}$",Relative(1),align=2E),Bounds(Min,Max),OutTicks); real[] datumz={0.5,1,1.5,2,2.5,3,3.5}; Label[] L=sequence(new Label(int i) { return YZ()*(Label(format("$z=%g$",datumz[i]), align=2currentprojection.vector()-1.5Z,Relative(1))); },datumz.length); pen fontsize=bp+fontsize(10); draw(L,lift(f,contour(f,(0,0),(5,10),datumz)), palette(datumz,Gradient(fontsize+red,fontsize+black)));
🔗graph3-fig011
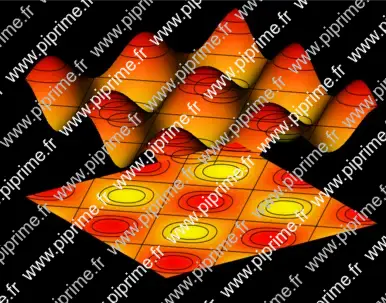
Show graph3/fig0110.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Surface | #Level set (3D) | #Contour | #Function (implicit) | #Palette | #Projection (3D) | #Axis (3D) | #Label (3D) | #Shading (3D) | #Shading
import graph3; import palette; import contour; size(14cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(-1,-1.5,0.75); currentlight=(-1,0,5); real a=1, b=1; real f(pair z) { return a*(6+sin(z.x/b)+sin(z.y/b));} real g(pair z){return f(z)-6a;} // The axes limits((0,0,4a),(14,14,8a)); xaxis3(Label("$x$",MidPoint),OutTicks()); yaxis3(Label("$y$",MidPoint),OutTicks(Step=2)); ticklabel relativelabel() { return new string(real x) {return (string)(x-6a);}; } zaxis3(Label("$z$",Relative(1),align=2E),Bounds(Min,Max),OutTicks(relativelabel())); // The surface surface s=surface(f,(0,0),(14,14),100,Spline); pen[] pens=mean(palette(s.map(zpart),Gradient(yellow,red))); // Draw the surface draw(s,pens); // Project the surface onto the XY plane. draw(planeproject(unitsquare3)*s,pens,nolight); // Draw contour for "datumz" real[] datumz={-1.5, -1, 0, 1, 1.5}; guide[][] pl=contour(g,(0,0),(14,14),datumz); for (int i=0; i < pl.length; ++i) for (int j=0; j < pl[i].length; ++j) draw(path3(pl[i][j])); // Draw the contours on the surface draw(lift(f,pl)); if(!is3D()) shipout(bbox(3mm,Fill(black)));
🔗graph3-fig012

Show graph3/fig0120.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Projection (3D) | #Shading (3D)
import graph3; import palette; real sinc(real x){return x != 0 ? sin(x)/x : 1;} real f(pair z){ real value = (sinc(pi*z.x)*sinc(pi*z.y))**2; return value^0.25; } currentprojection=orthographic(0,0,1); size(10cm,0); surface s=surface(f,(-5,-5),(5,5),100,Spline); s.colors(palette(s.map(zpart),Gradient((int)2^11 ... new pen[]{black,white}))); draw(planeproject(unitsquare3)*s,nolight);
🔗graph3-fig013

From TeXgraph exemples.
Show graph3/fig0130.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Shading (3D)
settings.render=0; import graph3; import palette; size(10cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(2,-2,2.5); real f(pair z) { real u=z.x, v=z.y; return (u/2+v)/(2+cos(u/2)*sin(v)); } surface s=surface(f,(0,0),(14,14),150,Spline); draw(s,mean(palette(s.map(zpart),Gradient(yellow,red)))); if(!is3D()) shipout(bbox(3mm,Fill(black)));
🔗graph3-fig014

From TeXgraph exemples.
Show graph3/fig0140.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Shading (3D)
settings.render=0; import graph3; import palette; size(15cm,0); currentprojection=orthographic(2,-2,2.5); real f(pair z) { real u=z.x, v=z.y; return (u/2+v)/(2+cos(u/2)*sin(v)); } surface s=surface(f,(0,0),(14,14),50,Spline); s.colors(palette(s.map(zpart),Gradient(yellow,red))); draw(s); if(!is3D()) shipout(bbox(3mm,Fill(black)));
🔗graph3-fig015

Show graph3/fig0150.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Shading (3D) | #Array | #Spherical harmonics
settings.render=0; import graph3; size(15cm); currentprojection=orthographic(4,2,4); real r(real Theta, real Phi){return 1+0.5*(sin(2*Theta)*sin(2*Phi))^2;} triple f(pair z) {return r(z.x,z.y)*expi(z.x,z.y);} pen[] pens(triple[] z) { return sequence(new pen(int i) { real a=abs(z[i]); return a < 1+1e-3 ? black : interp(blue, red, 2*(a-1)); },z.length); } surface s=surface(f,(0,0),(pi,2pi),100,Spline); // Interpolate the corners, and coloring each patch with one color // produce some artefacts draw(s,pens(s.cornermean())); if(!is3D()) shipout(bbox(3mm,Fill(black)));
🔗graph3-fig016

Show graph3/fig0160.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Shading (3D) | #Array | #Spherical harmonics
settings.render=0; import graph3; size(15cm); currentprojection=orthographic(4,2,4); real r(real Theta, real Phi){return 1+0.5*(sin(2*Theta)*sin(2*Phi))^2;} triple f(pair z) {return r(z.x,z.y)*expi(z.x,z.y);} pen[][] pens(triple[][] z) { pen[][] p=new pen[z.length][]; for(int i=0; i < z.length; ++i) { triple[] zi=z[i]; p[i]=sequence(new pen(int j) { real a=abs(zi[j]); return a < 1+1e-3 ? black : interp(blue, red, 2*(a-1));}, zi.length); } return p; } surface s=surface(f,(0,0),(pi,2pi),100,Spline); // Here we interpolate the pens, this looks smoother, with fewer artifacts draw(s,mean(pens(s.corners()))); if(!is3D()) shipout(bbox(3mm,Fill(black)));
🔗graph3-fig017
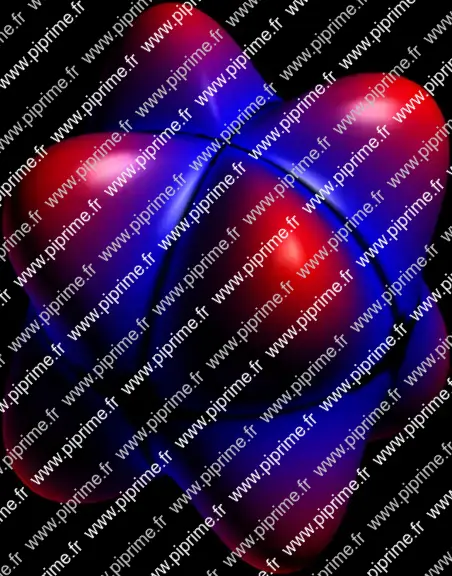

Show graph3/fig0170.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Shading (3D) | #Array | #Spherical harmonics
import graph3; size(16cm, 0); currentprojection=orthographic(4, 2, 4); real r(real Theta, real Phi){return 1+0.5*(sin(2*Theta)*sin(2*Phi))^2;} triple f(pair z) {return r(z.x, z.y)*expi(z.x, z.y);} pen[][] pens(triple[][] z) { pen[][] p=new pen[z.length][]; for(int i=0; i < z.length; ++i) { triple[] zi=z[i]; p[i]=sequence(new pen(int j) { real a=abs(zi[j]); return a < 1+1e-3 ? black : interp(blue, red, 2*(a-1));}, zi.length); } return p; } surface s=surface(f, (0, 0), (pi, 2pi), 100, Spline); // Here we determine the colors of vertexes (vertex shading). // Since the PRC output format does not support vertex shading of Bezier surfaces, PRC patches // are shaded with the mean of the four vertex colors. s.colors(pens(s.corners())); draw(s); if(!is3D()) shipout(bbox(1mm, Fill(black)));
🔗graph3-fig018

The spherical harmonics are the angular portion of the solution to Laplace's equation in spherical coordinates where azimuthal symmetry is not present.
The spherical harmonics are defined by:
where and is the Legendre polynomial.
Source
Show graph3/fig0180.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Graph3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Palette | #Surface | #Shading (3D) | #Spherical harmonics
import palette; import math; import graph3; typedef real fct(real); typedef pair zfct2(real,real); typedef real fct2(real,real); real binomial(real n, real k) { return gamma(n+1)/(gamma(n-k+1)*gamma(k+1)); } real factorial(real n) { return gamma(n+1); } real[] pdiff(real[] p) { // p(x)=p[0]+p[1]x+...p[n]x^n // retourne la dérivée de p real[] dif; for (int i : p.keys) { if(i != 0) dif.push(i*p[i]); } return dif; } real[] pdiff(real[] p, int n) { // p(x)=p[0]+p[1]x+...p[n]x^n // dérivée n-ième de p real[] dif={0}; if(n >= p.length) return dif; dif=p; for (int i=0; i < n; ++i) dif=pdiff(dif); return dif; } fct operator *(real y, fct f) { return new real(real x){return y*f(x);}; } zfct2 operator +(zfct2 f, zfct2 g) {// Défini f+g return new pair(real t, real p){return f(t,p)+g(t,p);}; } zfct2 operator -(zfct2 f, zfct2 g) {// Défini f-g return new pair(real t, real p){return f(t,p)-g(t,p);}; } zfct2 operator /(zfct2 f, real x) {// Défini f/x return new pair(real t, real p){return f(t,p)/x;}; } zfct2 operator *(real x,zfct2 f) {// Défini x*f return new pair(real t, real p){return x*f(t,p);}; } fct fct(real[] p) { // convertit le tableau des coefs du poly p en fonction polynôme return new real(real x){ real y=0; for (int i : p.keys) { y += p[i]*x^i; } return y; }; } real C(int l, int m) { if(m < 0) return 1/C(l,-m); real OC=1; int d=l-m, s=l+m; for (int i=d+1; i <=s ; ++i) OC *= i; return 1/OC; } int csphase=-1; fct P(int l, int m) { // Polynôme de Legendre associé // http://mathworld.wolfram.com/LegendrePolynomial.html if(m < 0) return (-1)^(-m)*C(l,-m)*P(l,-m); real[] xl2; for (int k=0; k <= l; ++k) { xl2.push((-1)^(l-k)*binomial(l,k)); if(k != l) xl2.push(0); } fct dxl2=fct(pdiff(xl2,l+m)); return new real(real x){ return (csphase)^m/(2^l*factorial(l))*(1-x^2)^(m/2)*dxl2(x); }; } zfct2 Y(int l, int m) {// http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harmonique_sph%C3%A9rique#Expression_des_harmoniques_sph.C3.A9riques_normalis.C3.A9es return new pair(real theta, real phi) { return sqrt((2*l+1)*C(l,m)/(4*pi))*P(l,m)(cos(theta))*expi(m*phi); }; } real xyabs(triple z){return abs(xypart(z));} size(16cm); currentprojection=orthographic(0,1,1); zfct2 Ylm; triple F(pair z) { // real r=0.75+dot(0.25*I,Ylm(z.x,z.y)); // return r*expi(z.x,z.y); real r=abs(Ylm(z.x,z.y))^2; return r*expi(z.x,z.y); } int nb=4; for (int l=0; l < nb; ++l) { for (int m=0; m <= l; ++m) { Ylm=Y(l,m); surface s=surface(F,(0,0),(pi,2pi),60); s.colors(palette(s.map(xyabs),Rainbow())); triple v=(-m,0,-l); draw(shift(v)*s); label("$Y_"+ string(l) + "^" + string(m) + "$:",shift(X/3)*v); } }
🔗grid3-fig001
Show grid3/fig0100.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Grid3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Grid (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import grid3; size(10cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(0.25, 1, 0.25); limits((-2,-2,0), (0,2,2)); grid3( pic=currentpicture, // picture (default=currentpicture) gridroutine=XYZgrid( // gridtype3droutine or gridtype3droutine [] (alias gridtype3droutines) // or gridtype3droutines []: // The routine(s) to draw the grid(s); // the values can be as follows: // * XYgrid : draw grid from X in direction of Y // * YXgrid : draw grid from Y in direction of X // etc... // * An array of previous values XYgrid, YXgrid, ... // * XYXgrid : draw XYgrid and YXgrid grids // * YXYgrid : draw XYgrid and YXgrid grids // * ZXZgrid : draw ZXgrid and XZgrid grids // * YX_YZgrid : draw YXgrid and YZgrid grids // * XY_XZgrid : draw XYgrid and XZgrid grids // * YX_YZgrid : draw YXgrid and YZgrid grids // * An array of previous values XYXgrid, YZYgrid, ... // * XYZgrid : draw XYXgrid, ZYZgrid and XZXgrid grids. pos=Relative(0)), // position (default=Relative(0)) : // this is the position of the grid relatively to // the perpendicular axe of the grid. // If 'pos' is a the real, 'pos' is a coordinate relativly to this axe. // Alias 'top=Relative(1)', 'middle=Relative(0.5)' // and 'bottom=Relative(0)' can be used as value. // Following arguments are similar as the function 'Ticks'. N=0, // int (default=0) n=0, // int (default=0) Step=0, // real (default=0) step=0, // real (default=0) begin=true, // bool (default=true) end=true, // bool (default=true) pGrid=grey, // pen (default=grey) pgrid=lightgrey, // pen (default=lightgrey) above=false // bool (default=false) ); xaxis3(Label("$x$",position=EndPoint,align=S), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks()); yaxis3(Label("$y$",position=EndPoint,align=S), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks()); zaxis3(Label("$z$",position=EndPoint,align=(0,0.5)+W), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks(beginlabel=false));
🔗grid3-fig002

Show grid3/fig0200.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Grid3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Grid (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import grid3; size(10cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(0.25, 1, 0.25); limits((-2,-2,0), (0,2,2)); scale(Linear, Linear, Log(automax=false)); grid3(XZXgrid); grid3(XYXgrid); xaxis3(Label("$x$",position=EndPoint,align=S), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks()); yaxis3(Label("$y$",position=EndPoint,align=S), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks()); zaxis3(Label("$z$",position=EndPoint,align=(0,0.5)+W), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks(beginlabel=false));
🔗grid3-fig003
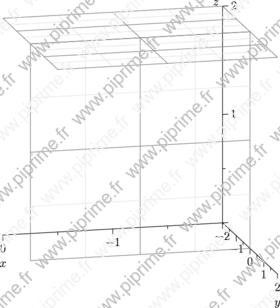
Show grid3/fig0300.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Grid3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Grid (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import grid3; size(10cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(0.25, 1, 0.25); limits((-2,-2,0), (0,2,2)); grid3(new grid3routines [] {XYXgrid(Relative(1)), XZXgrid(0)}); xaxis3(Label("$x$",position=EndPoint,align=S), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks()); yaxis3(Label("$y$",position=EndPoint,align=S), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks()); zaxis3(Label("$z$",position=EndPoint,align=(0,.5)+W), Bounds(Min,Min), OutTicks(beginlabel=false));
🔗grid3-fig004

Show grid3/fig0400.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Grid3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Grid (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import grid3; size(10cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(0.25, 1, 0.25); limits((-2,-2,0),(0,2,2)); grid3(new grid3routines [] {XYXgrid(-0.5), XYXgrid(1.5)}, pGrid=new pen[] {red, blue}, pgrid=new pen[] {0.5red, 0.5blue}); xaxis3(Label("$x$",position=EndPoint,align=Z), YZEquals(-2,0), OutTicks()); yaxis3(Label("$y$",position=EndPoint,align=Z), XZEquals(-2,0), OutTicks()); zaxis3(Label("$z$",position=EndPoint,align=X), XYEquals(-2,-2), OutTicks(Label("",align=-X-Y)));
🔗grid3-fig005

Show grid3/fig0500.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Grid3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Grid (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import grid3; size(10cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(0.25,1,0.25); limits((-2,-2,0),(0,2,2)); real Step=0.5, step=0.25; xaxis3(Label("$x$",position=EndPoint,align=Z), YZEquals(-2,0), InOutTicks(Label(align=0.5*(Z-Y)), Step=Step, step=step, gridroutine=XYgrid, pGrid=red, pgrid=0.5red)); yaxis3(Label("$y$",position=EndPoint,align=Z), XZEquals(-2,0), InOutTicks(Label(align=-0.5*(X-Z)), Step=Step, step=step, gridroutine=YXgrid, pGrid=red, pgrid=0.5red)); zaxis3("$z$", XYEquals(-1,0), OutTicks(Label(align=-0.5*(X+Y))));
🔗grid3-fig006

Show grid3/fig0600.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Grid3.asy
Tags : #Graph (3D) | #Grid (3D) | #Axis (3D)
import grid3; size(10cm,0,IgnoreAspect); currentprojection=orthographic(0.25,1,0.25); limits((-2,-2,0),(0,2,2)); xaxis3(Label("$x$",position=EndPoint,align=Z), YZEquals(-2,0), OutTicks(Label(align=0.5*(Z-Y)),Step=0.5, gridroutine=XYgrid)); yaxis3(Label("$y$",position=EndPoint,align=-X), XZEquals(-2,0), InOutTicks(Label(align=0.5*(Z-X)),N=8,n=2, gridroutine=YX_YZgrid)); zaxis3("$z$", OutTicks(ZYgrid));
🔗tube-fig004

Show tube/fig0040.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Graph (3D)
import tube; import graph3; size(10cm,0); currentprojection=perspective(4,3,4); triple f(real t){ return t*Z+(cos(2pi*t),sin(2pi*t),0)/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2); } path3 p=graph(f,0,2.7,operator ..); draw(tube(p,scale(0.2)*polygon(5)), purple);
🔗tube-fig005

Show tube/fig0050.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Graph (3D) | #Shading (3D)
import tube; import graph3; size(10cm,0); currentprojection=perspective(4,3,4); real x(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*cos(2pi*t);} real y(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*sin(2pi*t);} real z(real t) {return t;} path3 p=graph(x,y,z,0,2.7,operator ..); path section=scale(0.2)*polygon(5); // tube.asy defines a "colored path". // The value of coloredtype may be coloredSegments or coloredNodes. // Here the path scale(0.2)*polygon(5) has fixed colored SEGMENTS. coloredpath cp=coloredpath(section, // The array of pens become automatically cyclic. new pen[]{0.8*red, 0.8*blue, 0.8*yellow, 0.8*purple, black}, colortype=coloredSegments); // Draw the tube, each SEGMENT of the section is colored. draw(tube(p,cp));
🔗tube-fig006

Show tube/fig0060.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Graph (3D) | #Shading (3D)
import tube; import graph3; size(10cm,0); currentprojection=perspective(4,3,4); real x(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*cos(2pi*t);} real y(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*sin(2pi*t);} real z(real t) {return t;} path3 p=graph(x,y,z,0,2.7,operator ..); path section=scale(0.2)*polygon(5); // Here the path scale(0.2)*polygon(5) has colored NODES. coloredpath cp=coloredpath(section, new pen[]{0.8*red, 0.8*blue, 0.8*yellow, 0.8*purple, black}, colortype=coloredNodes); // Draw the tube, each NODE of the section is colored. draw(tube(p,cp));
🔗tube-fig007

Show tube/fig0070.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Graph (3D) | #Shading (3D)
import tube; import graph3; size(10cm,0); currentprojection=perspective(4,3,4); real x(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*cos(2pi*t);} real y(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*sin(2pi*t);} real z(real t) {return t;} path3 p=graph(x,y,z,0,2.7,operator ..); path section=scale(0.2)*polygon(5); // Define a pen wich depends of a real t. t represent the "reltime" of the path3 p. pen pen(real t){ return interp(red,blue,1-2*abs(t-0.5)); } // Here the section has colored segments (by default) depending to reltime. draw(tube(p,coloredpath(section,pen)));
🔗tube-fig008

Show tube/fig0080.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Graph (3D) | #Shading (3D)
import tube; import graph3; size(12cm,0); currentprojection=perspective((-1,1,1)); int p=7, q=3; real n=p/q; real a=1, b=1; real x(real t){return a*cos(t);} real y(real t){return a*sin(t);} real z(real t){return b*cos(n*t);} real R(real t){ real st2=(n*sin(n*t))^2; return a*(1+st2)^(1.5)/sqrt(1+st2+n^4*cos(n*t)^2); // return -a*(1+st2)^(1.5)/sqrt(1+st2+n^4*cos(n*t)^2); // Signed radius curvature } real mt=q*2*pi; path3 p=graph(x,y,z,0,mt,operator ..)..cycle; real m=R(0), M=R(0.5*pi/n); // Define a pen depending to the radius curvature of graph(x,y,z) at reltime t pen curvaturePen(real t){ real r=abs(R(t*mt)-m)/(M-m); return interp(red,blue,r); } // Draw the tube, colors depend of the radius curvature R. draw(tube(p,coloredpath(scale(0.1)*unitcircle, curvaturePen)));
🔗tube-fig009

Show tube/fig0090.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Graph (3D) | #Shading (3D) | #Array
import tube; import graph3; size(10cm,0); currentprojection=perspective(4,3,4); real x(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*cos(2pi*t);} real y(real t) {return (1/sqrt(1+0.5*t^2))*sin(2pi*t);} real z(real t) {return t;} path3 p=graph(x,y,z,0,2.7,operator ..); path section=scale(0.2)*polygon(4); // Define an array of pen wich depends of a real t. t represent the "reltime" of the path3 p. pen[] pens(real t){ return new pen[] {interp(blue,red,t), interp(orange,yellow,t), interp(green,orange,t), interp(red,purple,t)}; } // "pen[] pens(real t)" allows to color each nodes or segments with a real parameter (the reltime) // Note that all arrays of pens are convert to cyclical arrays. draw(tube(p,coloredpath(section, pens, colortype=coloredNodes)));
🔗tube-fig021

Show tube/fig0210.asy on Github.
Generated with Asymptote 3.00-0.
Categories : Examples 3D | Tube.asy
Tags : #Tube | #Palette | #Shading (3D) | #Graph (3D)
import tube; import graph3; import palette; size(12cm,0); currentprojection=perspective(1,1,1); int e=1; real x(real t) {return cos(t)+2*cos(2t);} real y(real t) {return sin(t)-2*sin(2t);} real z(real t) {return 2*e*sin(3t);} path3 p=scale3(2)*graph(x,y,z,0,2pi,50,operator ..)&cycle; pen[] pens=Rainbow(15); pens.push(black); for (int i=pens.length-2; i >= 0 ; --i) pens.push(pens[i]); path sec=subpath(Circle(0,1.5,2*pens.length),0,pens.length); coloredpath colorsec=coloredpath(sec, pens,colortype=coloredNodes); draw(tube(p,colorsec));